 Dr. Chenraj Roychand
Dr. Chenraj Roychand A distinguished Indian educationist, entrepreneur, angel investor and philanthropist with over 40 years of experience...
 Dr. Chenraj Roychand
Dr. Chenraj Roychand  Sri. Achalchand Jain
Sri. Achalchand Jain  Dr. Ganesh D. B.
Dr. Ganesh D. B.  Master of Business Administration (MBA)
Master of Business Administration (MBA)
 Master of Business Administration (MBA) - 120
Master of Business Administration (MBA) - 120
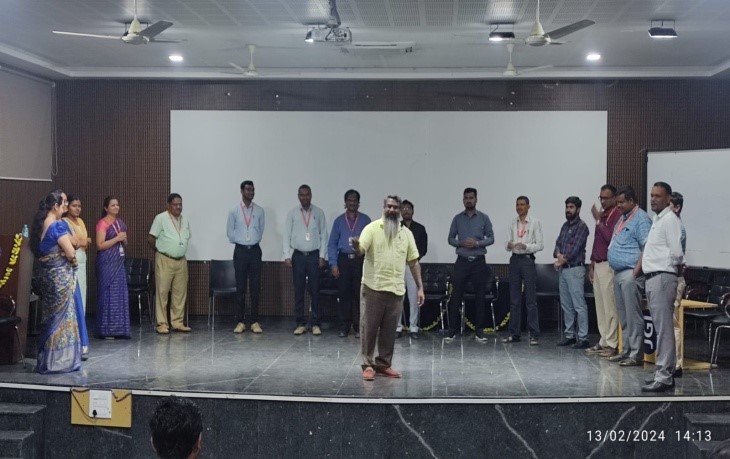
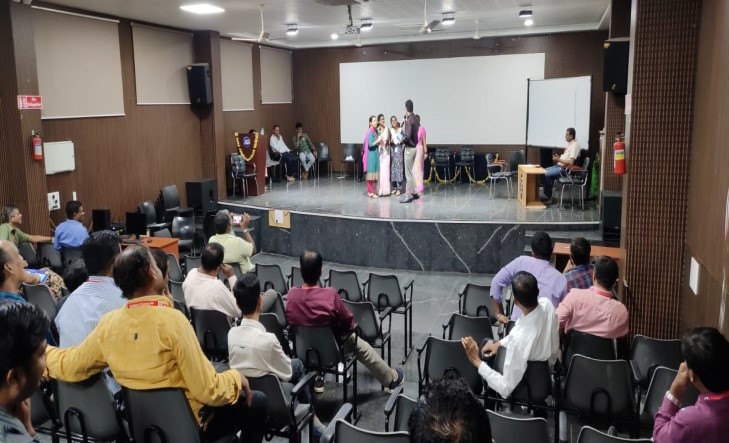
IIC in association with IQAC, Jain Institute of Technology Davanagere has organized Workshop on “Entrepreneurship Skill, Attitude, and Behavior Development” on 14 February 2024.
Trainers Mr. Dominic Avinash and Neville Kevin Rodrigues conducted the workshop. Dr. Manjappa Sarathi S , Advisor JIT outlined the needs of Innovation Design.
Workshop on Entrepreneurship Skill, Attitude, and Behavior Development aims to equip participants with the mindset, skills, and behaviors necessary to succeed as entrepreneurs. Content covered in a workshop includes:
1. Introduction to Entrepreneurship:
2. Developing the Entrepreneurial Mindset:
3. Skills for Entrepreneurial Success:
4. Attitude and Behavior Development:
5. Entrepreneurial Vision and Goal Setting:
6. Opportunity Identification and Validation:
7. Business Model Development:
8. Building a Strong Entrepreneurial Network:
9. Overcoming Challenges and Resilience:
10. Action Planning and Next Steps:
11. Hands-on Activities:
By covering these topics and incorporating interactive exercises and discussions, participants enhanced their entrepreneurial mindset, skills, and behaviors, setting a solid foundation for pursuing their entrepreneurial aspirations.





IIC in association with IQAC, Jain Institute of Technology Davanagere has organized Expert talk on Process of “Innovation Development, Technology Readiness Level (TRL); Commercialization of Lab Technologies & Tech-Transfer” on 12 February 2024. Program had a wonderful beginning by invoking almighty by Prof. Pavitra P raykar and team department of basic science Prof. Archana K N, Department of CS&E welcomed the gathering. FDP Insights were given by Dr.MadhukeshwaraN ,Dean Academics.
Chief guest Mr. R S Hiremath, CEO, Flexitron, Bengaluru gave expert talk on Process of “Innovation Development, Technology Readiness Level (TRL); Commercialization of Lab Technologies & Tech-Transfer”
Dr. Manjappa Sarathi S , Advisor JIT outlined the needs of Innovation. Dr Ganesh D B, principal and Director gave presidential remarks. Professor Latharani T R , Assistant professor department of Computer Science and Engineering cast vote of thanks. Prof G C Divya, Prof .Usha K were the hosts of Inaugural ceremony. Dr.Ganesh N Y, department of chemistry co ordinated the event.
Mr. R.S.Hiremath is a Mechanical engineer, based in Bangalore.
He served at KSCST(Indian Institute of Science) in Bangalore for 3 years contributing to various innovative and new projects in the field of alternative energy, rural industries, and energy conservation.
His ‘hands-on’ experience working in the rural areas where his work carried him became the foundation for starting a company called FLEXITRON a social enterprise that focused on developing and marketing products for the people at the bottom of the pyramid i.e. the poorest population of the world, artisans, and empowerment tools for the rural enterprises.
Innovation has been the bottom line of all his activities, and he has to his credit over 675 innovations, with 225 commercialized. Millions of people around the world use his commercialized products.
He has been conferred with 4 National awardsby the Government of India for his contributions to society in the form ofhis various Innovations.
He now dedicates most of his time to delivering lectures, conducting workshops on social innovations, mentoring Social innovators globally and hand-holding startups.
COMMUNICATION DETAILS
R.S. Hiremath
1234, 22A Main, 11 A Cross, Sector-1
HSR Layout, BANGALORE – 560 102
Ph. : 09845113109,
e-mail : flexitron@yahoo.com
Web site : www.flexitron.com
The process of innovation development, technology readiness level (TRL), and commercialization of lab technologies, along with technology transfer, typically involves several stages and steps.
1. Idea Generation and Concept Development:
Throughout this process, collaboration between researchers, developers, entrepreneurs, investors, and industry partners is crucial for successful innovation development, commercialization, and technology transfer. Additionally, regulatory compliance and ethical considerations play significant roles, especially in highly regulated industries such as healthcare and biotechnology.
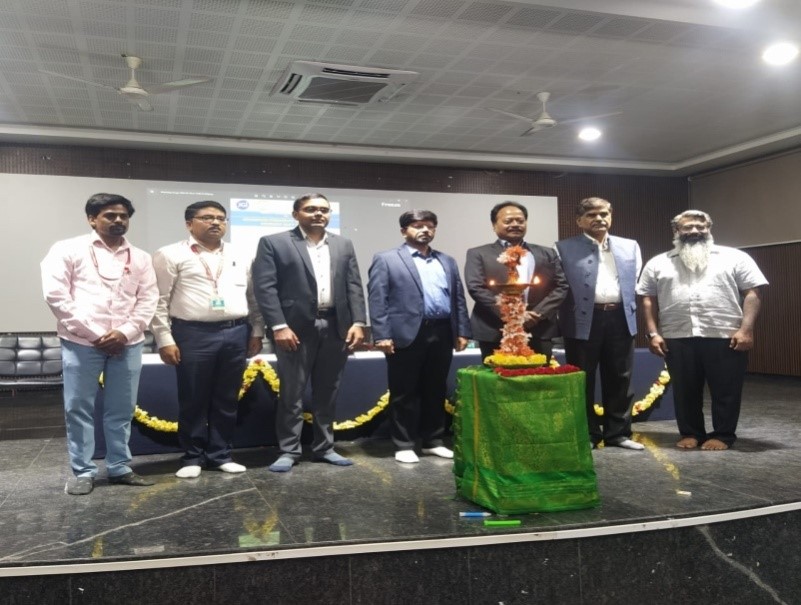
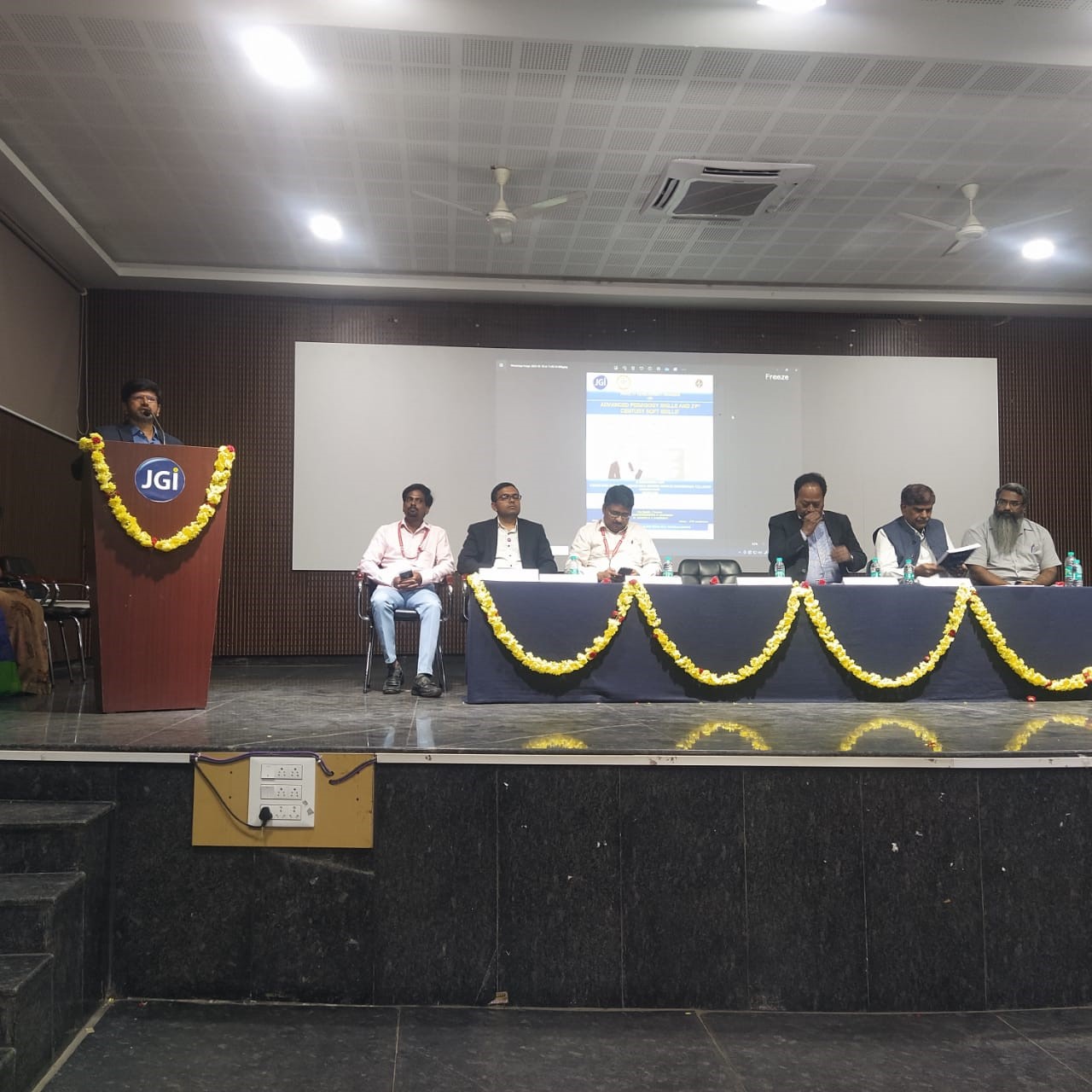





Department of Electrical & Electronics Engineering in association with IIC and IQAC of JITD, Davangere, organized Session on Problem Solving and Ideation Workshop on 22/09/2023.
Chief Guest Sri. Anil Kumar Nadiger Chairman Rachana Enercare Energy managers & Auditors, Resource Persons Sri Rajeev P Nadig EMS & IOT Consultant , Sri Dayanand Renewable Projects Manager , Guest of Honor Dr. Manjappa Sarathi, Advisor Jain Group of Institutions Director research SCEM Mangalore , Dr. Ganesh D B Prinicpal & Director, head of the Department Prof. Preetha P S, Event Coordinator Prof. Nandish B M, Forum Coordinator Prof. Chetan H R inaugurated the event by lightning the lamp .
All the Teaching and Non-Teaching faculty members coordinated the event. Final year Students participated in the workshop.
Morning Theoretical sessions on Problem Solving and Ideation were carried out by the resource persons and Demonstrations was carried out in the afternoon session. Quiz was organized for the participants and the prizes were distributed. Lunch was provided for the participants.








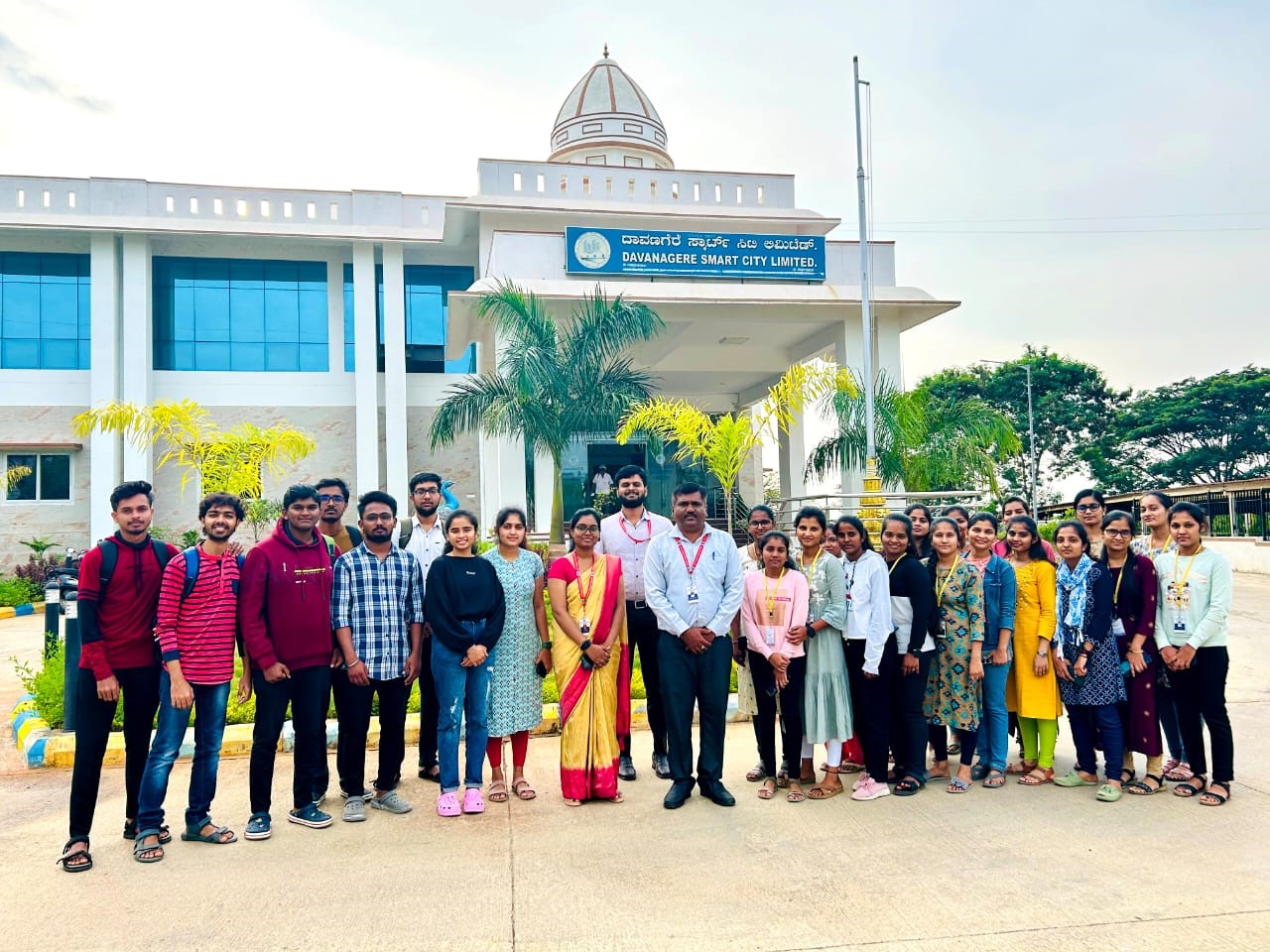
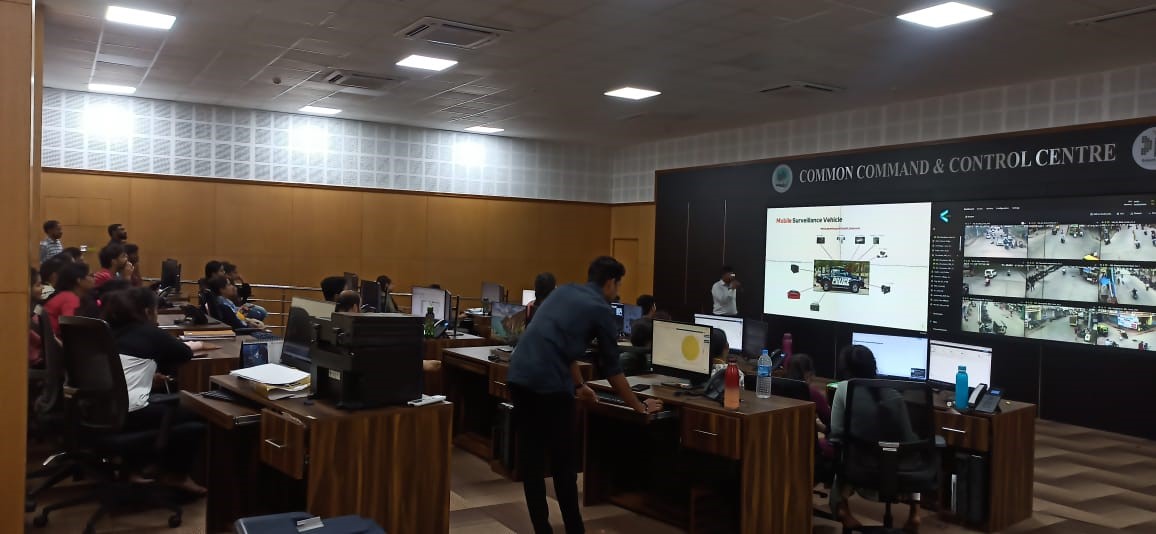
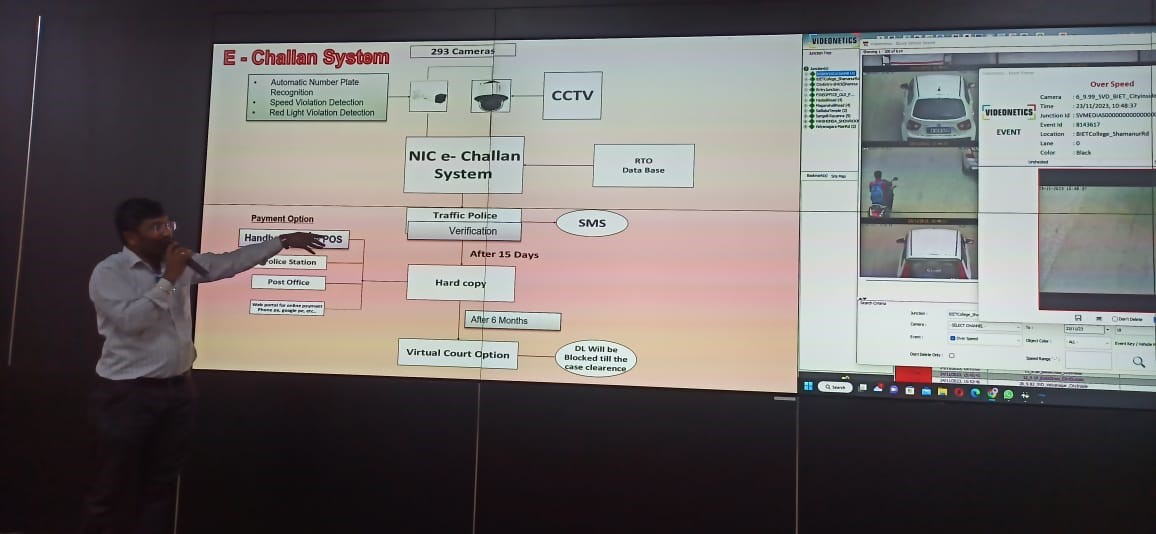
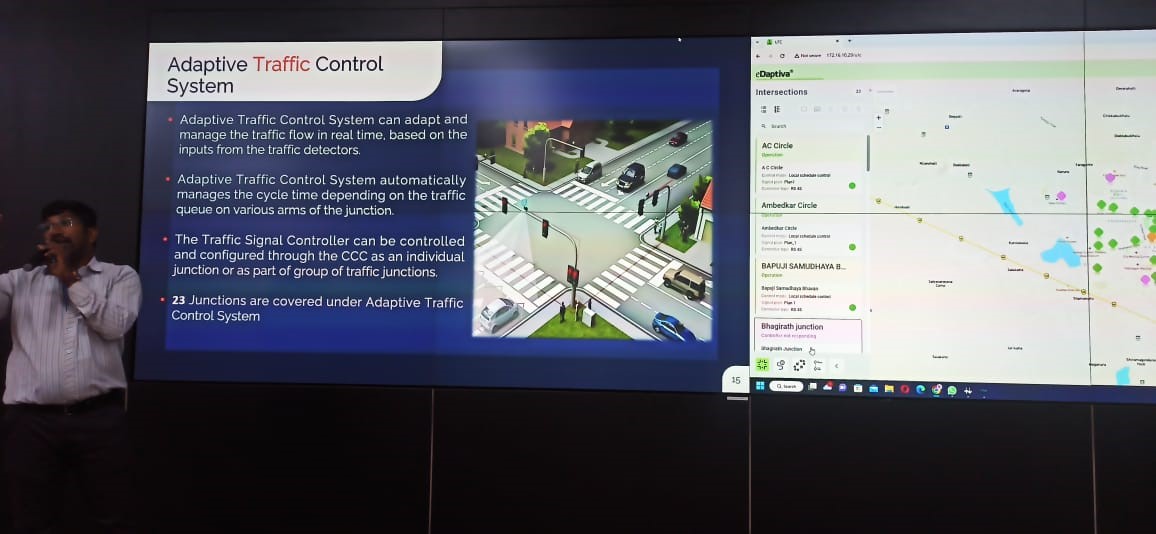
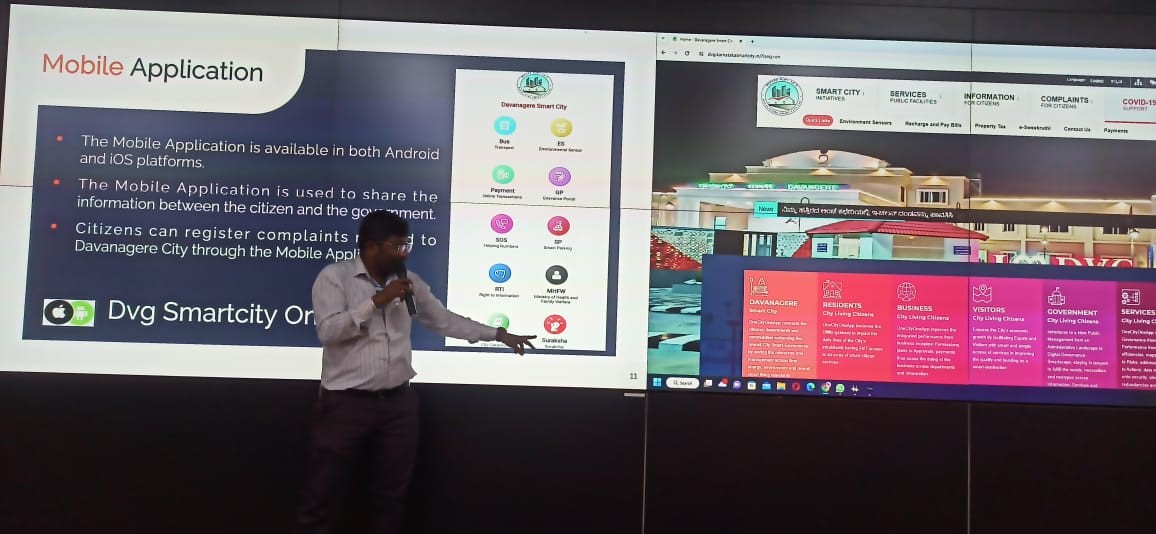
Field Visit to Davangere Smart City Private Limited
Department of Computer science and engineering in association with IIC, JITD organized field visit for 5th semester students to Davangere smart city Integrated command and control centre, Davanagere on 22 November 2023. Student’s gained knowledge about Davanagere smart city infrastructures and their usage, Challenges, problems and benefits to the public about smart city infrastructure. Dr.Prashantha G R, Prof.Sameer B, Prof.Usha K coordinated the visit.
Students gathered numerous challenges and problems in its quest to develop smart cities. Some of the key issues and challenges include:
Addressing these challenges requires a multi-faceted approach involving collaboration between government, private sector, academia, and civil society to develop holistic strategies for sustainable and inclusive urban development in India.








Viksit Bharat 2047 is the vision to transform India into a developed nation by 2047, the 100th year of independence. This vision encompasses various facets of development, such as economic growth, environmental sustainability, social progress, and good governance, to make India a developed nation by 2047. Students from E&CE branch of Jain Institute of Technology, Davangere participated in this program on 11th January, 2024. Under the leadership of Prime Minister Narendra Modi, the Union Government has introduced 'Vision Viksit Bharat@2047 - ,' envisioning India as a superpower, with the youth playing a pivotal role.Viksit Bharat prioritises inclusive development and social welfare to ensure everyone benefits from economic progress. The administration has launched several landmark initiatives to support disadvantaged populations, empower marginalised communities, and expand social security, healthcare, and education.




The Institution Innovation Council (IIC) and Department of Mechanical Engineering, Jain Institute of Technology (JIT), Davanagere, IQAC, ISTE, jointly organized a business plan event with respect to activity on " StUDENT’S BUSINESS PLAN " on 10-03-2022 @ Electrical Seminar Hall Classroom NO 226
The Bussiness plan presentation was organized by the Department of CS&E, Jain Institute of Technology, and Davangere on 10-3-2022.
The coordinator of the programme Mrs. Manjula.P addressed the gathering about the purpose and need of student’s participation in the presentation. Prof and Head Dr. Mouneshachari S addressed students about the advantage and the exposure students will get after active participation in these kinds of events. He also insisted on the student’s new idea and the projects that must implemented in future.
The participant Mr.Manjunatha of 3rd sem E&C dept gave feedback about the event and expressed how this event helped him to find a solution to different problems. Miss. shirisha of 3rd sem Mech also share the experience of the event, she told this event was very useful to understand how to present the concept and also what things we should add in the presentation .
Finally presidential address was done by principal and director Dr. Ganesh. D.B. He addressed about skill and new ideas students should develop in order to become competent.He also insisted on importance of students participation in these kinds of events to acquire important skills like communication, presentation etc.
Ms. Mizba of 3rd sem anchored the event. Vote of thanks was done by Ms. Rida, 3rd sem CSE. The presentation evaluation was started at 2.00pm by judges of various deparment .Judges evaluated the presentation and selected best three projects. The prizes are distributed to the winners in the valedictory function.
To create awareness regarding presentation- on 10th March.
Business plans typically include detailed information that can help improve your business’s chances of success, like:








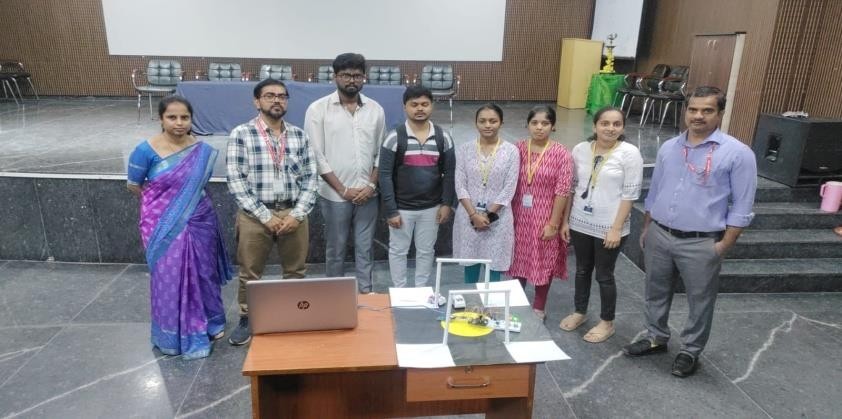
Students Innovative Projects selected for Yukthi Innovation Challenge from Jain Institute of Technology, Davangere participated in IIC Regional Meet, 2024 held at KLE, University Hubli on January, 19th 2024. AICTE Advisor Dr. Mamatarani Agarwal and Assistant Innovation Director Dipan Sahu presided as Guest to the Event.
Students Projects such as Smart Movable Road Divider, Smart Automation using IoT, Seeds Dryer system using Solar were displayed in the competition.




